Overview
You have applied a change in your MMSC servers, so you just want to check if the status of all servers in the nodes is correct for troubleshooting purposes. The following article contains the basic checks you must go through to narrow down issues related to the service's health.
Information
The basic Mercury health check includes the execution of the following steps:
- Checking the cluster status
- Checking Mercury processes
- Check Mercury mounted filesystem
- Check free disk space
- Checking Virtual IP addresses
- Checking the listening TCP port
- Checking open connections
- Checking memory used by mercury SMSM service
Checking the cluster status
Run the following command to get the cluster status:
pcs status
- Cluster nodes should be in online state
- Cluster services should be started
- No failed actions alert log
- No cluster services in failed state
- The cluster should not be in maintenance mode
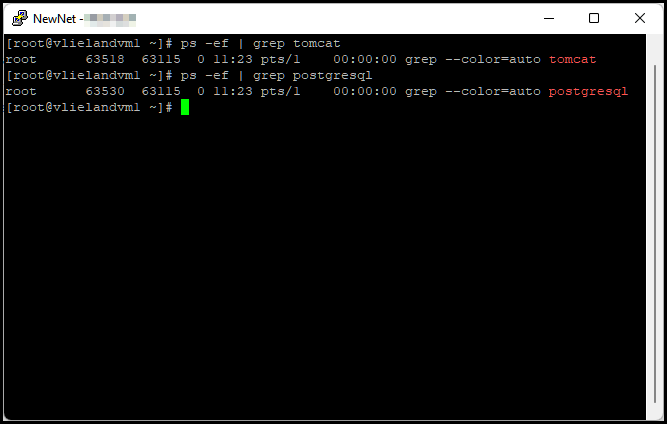
Checking Mercury processes
Run the following system command:
ps -ef
Java process: ps -ef | grep tomcat
Postgresql process: ps -ef | grep postgresql
- Processes should be running
Checking Mercury mounted filesystem
Run the following system command:
df -kh
- 3 mercury partitions shall be mounted
- /usr/mercury
- /var/mercury
- /var/log/mercury
Check free disk space
Run the following system command:
df -h
- Use percentage in the following three Mercury partitions shall not exceed 85%
- /usr/mercury
- /var/mercury
- /var/log/mercury
Checking Virtual IP addresses
Run the following system command:
IP address
- Virtual addresses/Secondary addresses are active
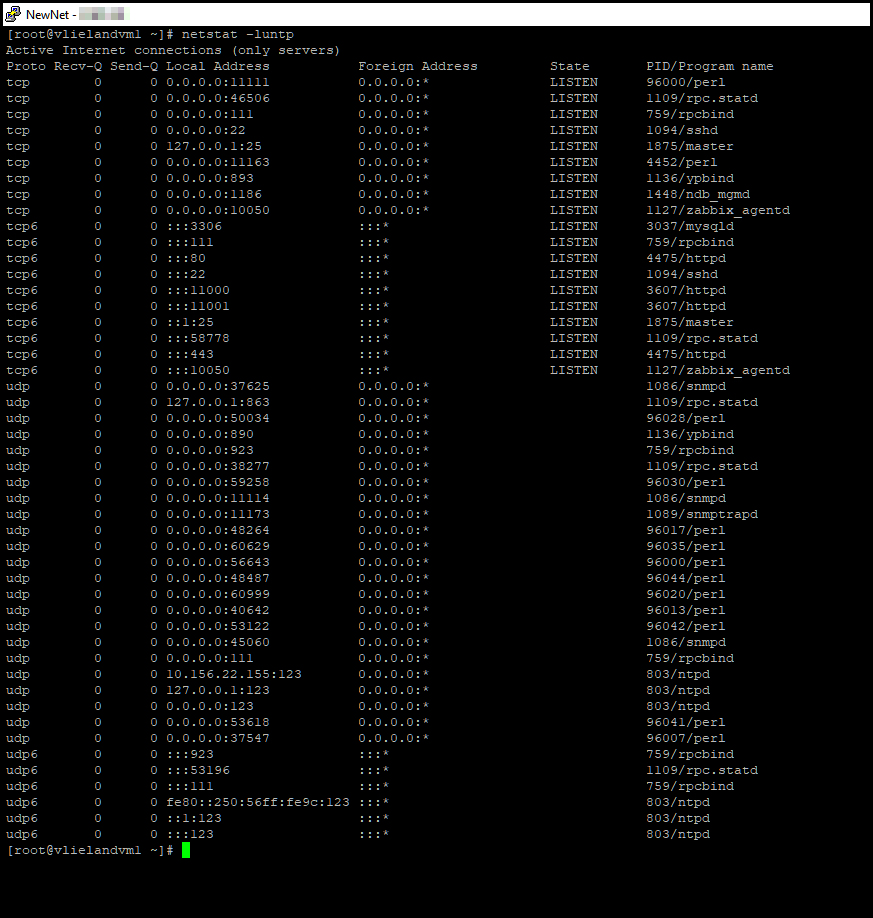
Checking the listening TCP port
Run the following system command:
netstat -luntp
You can grep (filter) the results by using the following structure:
WAPGW (p2p):
netstat -luntp | grep 8080
RADIUS:
netstat -luntp | grep 1813
SMSM:
netstat -luntp | grep 2950
MMSC (p2p):
netstat -luntp | grep 8081
MMSC (a2p):
netstat -luntp | grep 8080
- TCP ports should be opened. Bear in mind that you must grep by port. (for example, by greping 1813, you are looking if port 1813 is open and listening).
Checking open connections
Run the following commands to confirm the open and established connections (by port):
WAPGW (p2p):
netstat -an | grep ":80" | grep -E "ESTABLISHED|SYN_RECV" | wc -l
MMSC (p2p):
netstat -an | grep ":8081" | grep -E "ESTABLISHED|SYN_RECV" | wc -l
MMSC (a2p):
netstat -an | grep ":8080" | grep -E "ESTABLISHED|SYN_RECV" | wc -l
- The number of open connections shall not grow quickly
Checking the number of unsent messages in queues
Run system command (as mercury user):
psql mdg -c 'select queue_id, count(1) cnt from ddgtr where tr_flags < 32 group by queue_id;'
- The number of unsent messages in a queue should not grow quickly.
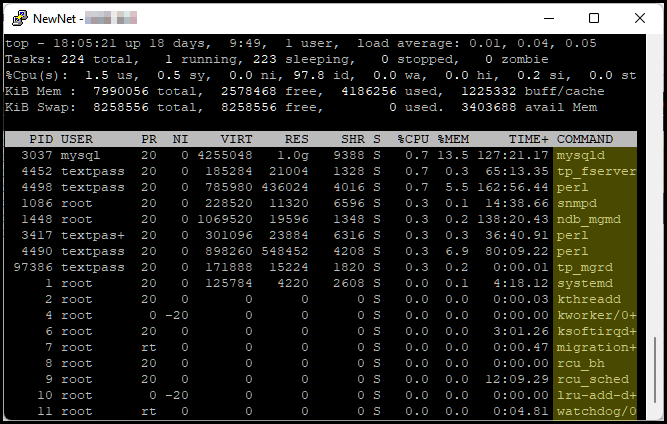
Checking memory used by mercury SMSM service
Run the following system command:
top
- Check that the memory usage of the SMSM process (yellow column) doesn’t exceed 1Gb.
Priyanka Bhotika
Comments